Do you want to know the full story behind the rope in the mystery picture the other day? On the recent Håkon Mosby cruise, we did a lot of mooring work, and that rope was part of a mooring that we recovered after it has been out in the Iceland Sea for two years.
So what are those moorings all about? The idea behind moorings is that it is super expensive to go out on research ships and that you can only stay out for a fairly short period of time compared to the amount of time you would like to cover with measurements. Therefore, installing instrumentation in the sea and leaving it out there for extended periods of time to measure and store data without anyone being close by, looking after it, gets you a lot of data that you could otherwise never obtain. Once a mooring is in the water, there is no communication with it at all until, after a year or two, we come back to pick up the instruments, read out the data and start on the science.
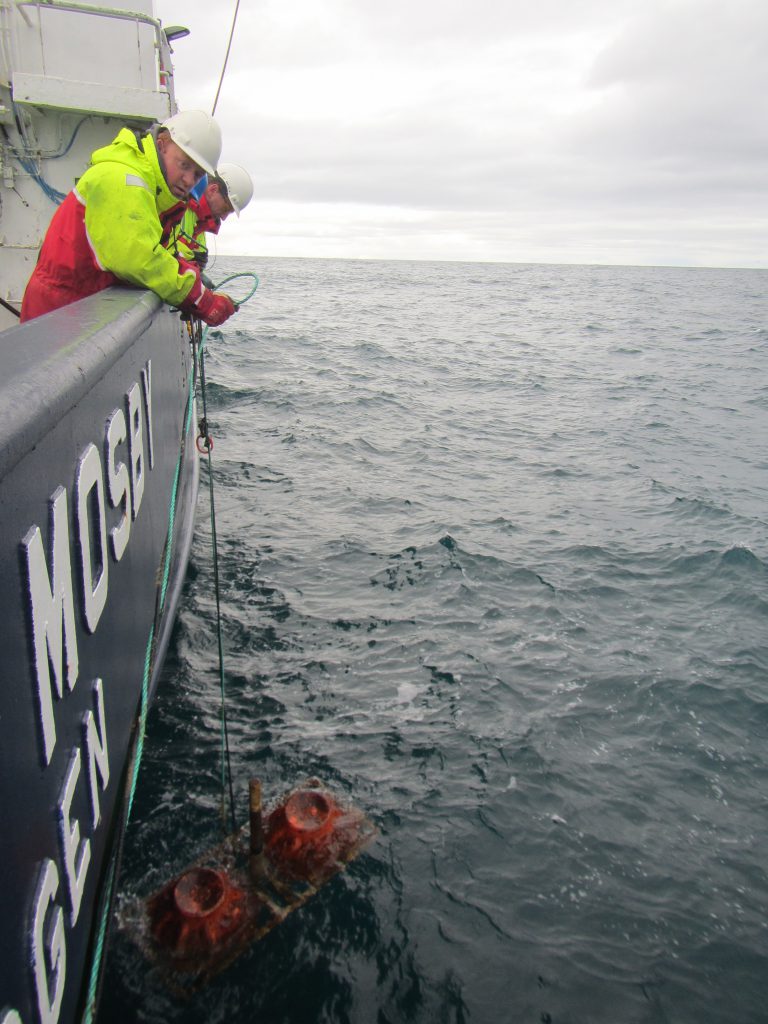
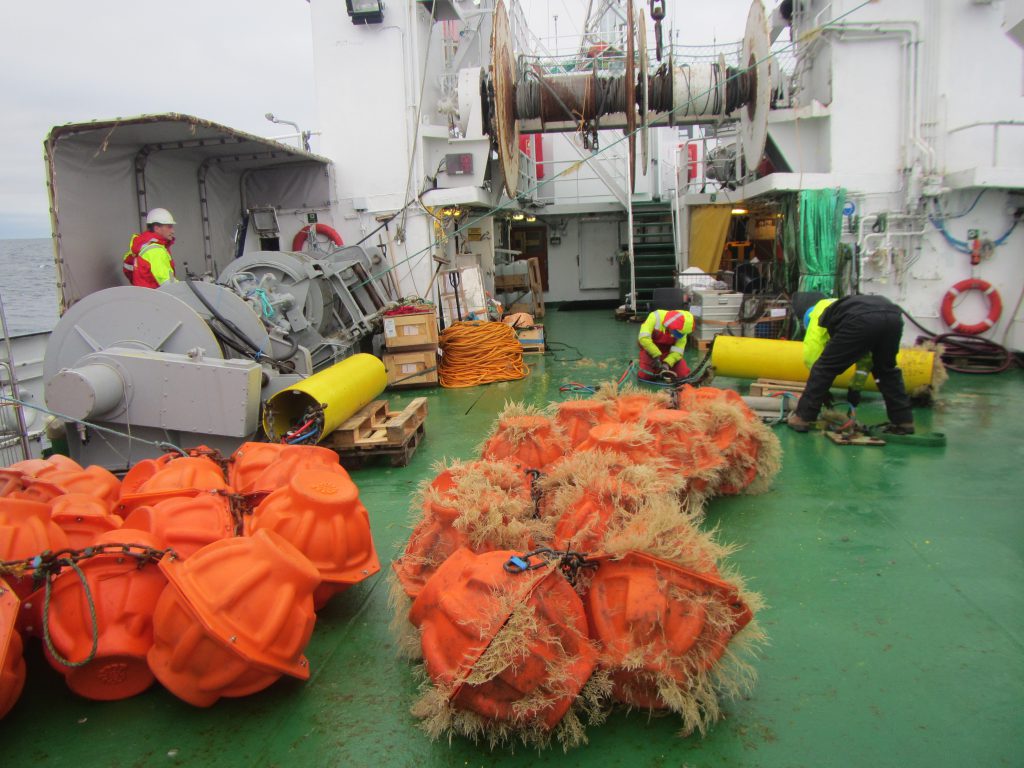
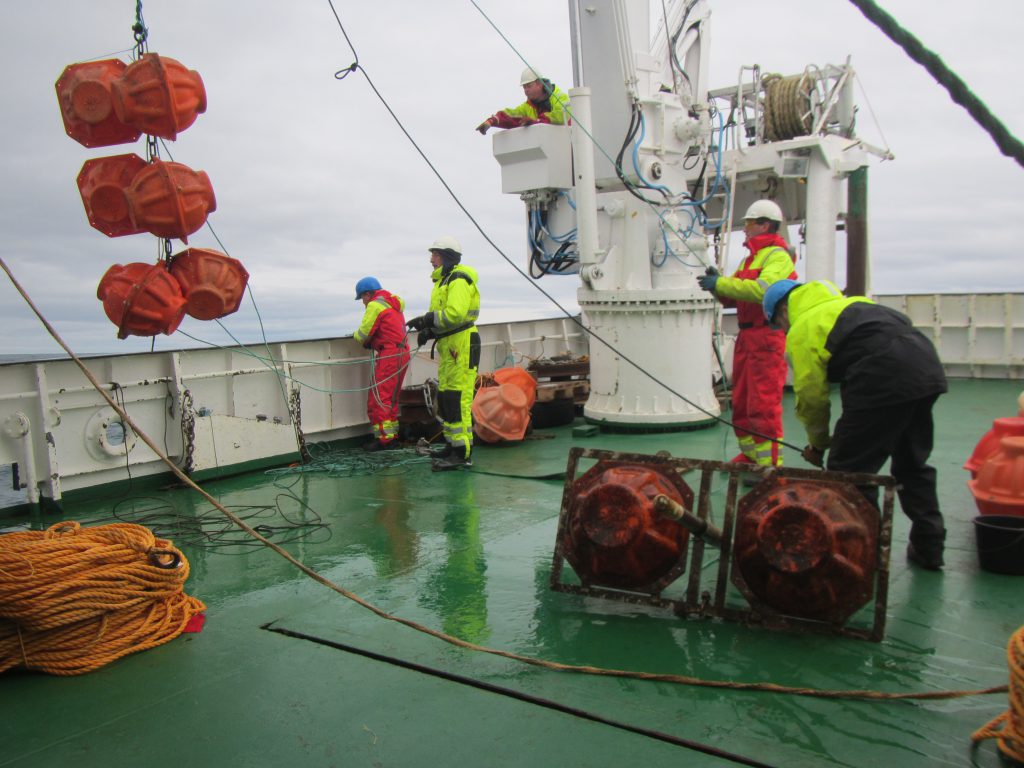
Moorings basically consist of a lot of rope. They are one or more long pieces of rope held down to the sea floor by a large metal anchor and then pulled in an upright position by large buoys that float at some depth underneath the sea surface. And then there are lots and lots of instruments attached to the ropes at different depths, most with their own buoyant orange floatation thingies [technical term] attached so that, if the ropes broke accidentally, they would float up to the surface and there is the (tiny) chance they might be recovered.
Below is a sketch of a mooring on the Kögur section (And check out the website http://kogur.whoi.edu for tons of information on that section!) to give you an idea of what those things look like (thanks, Kjetil, for letting me use the sketch, and thanks, Steinar, for the awesome work!). I was actually on both the cruise deploying that mooring in 2011 and recovering it in 2012 – check out the cruise blogs for those cruises, well worth a read even years later!
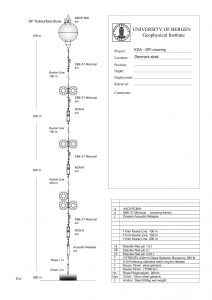
So now without further ado: on to deploying a mooring!
Before a mooring can be deployed, though, a lot of work goes into preparing ropes of the correct lengths with shackles in between where instruments or floatation thingies go.
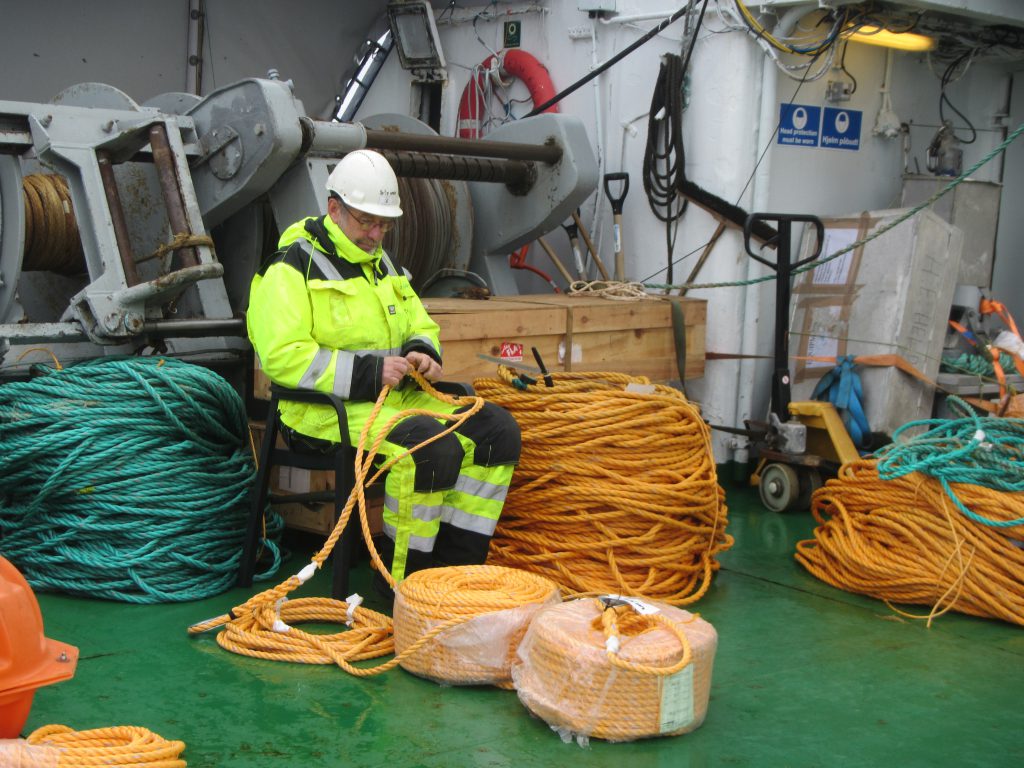

On the day the mooring is deployed, instruments get attached to the ropes in the correct spots, so they end up at the right depths in the water.
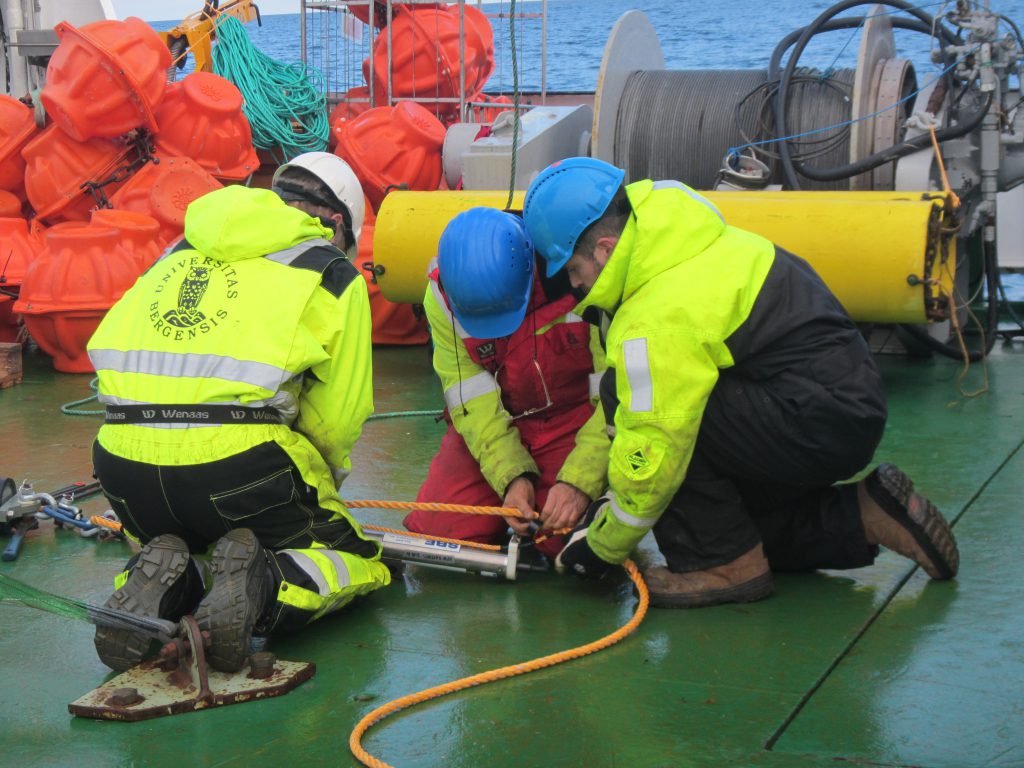

Since moorings are typically several hundred to thousands of meters long, instruments and floatation thingies cannot be attached beforehand and the whole thing then just be thrown out into the water. Instead, when a part of the mooring is ready, out it goes into the sea to make room on deck for the next one to be prepared to avoid creating a gigantic knot filled with very expensive instrumentation.
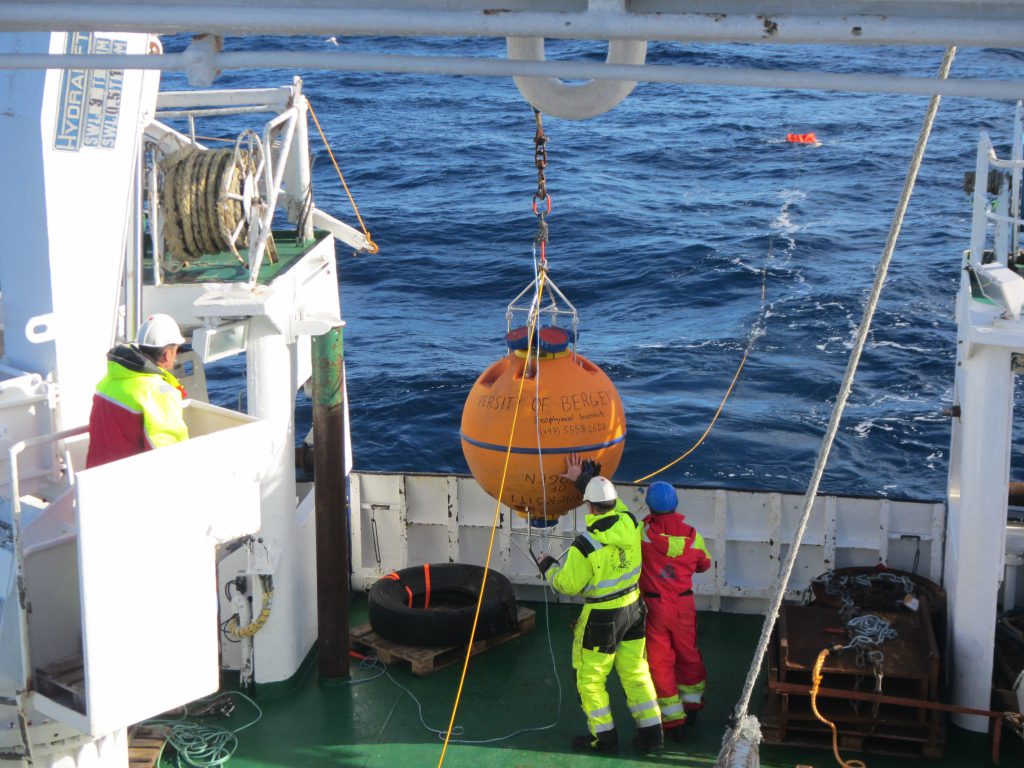

The whole thing has to be very well coordinated, since there are several cranes and winches involved, and many expensive instruments that are all to end up at a specified depth to measure specific features.

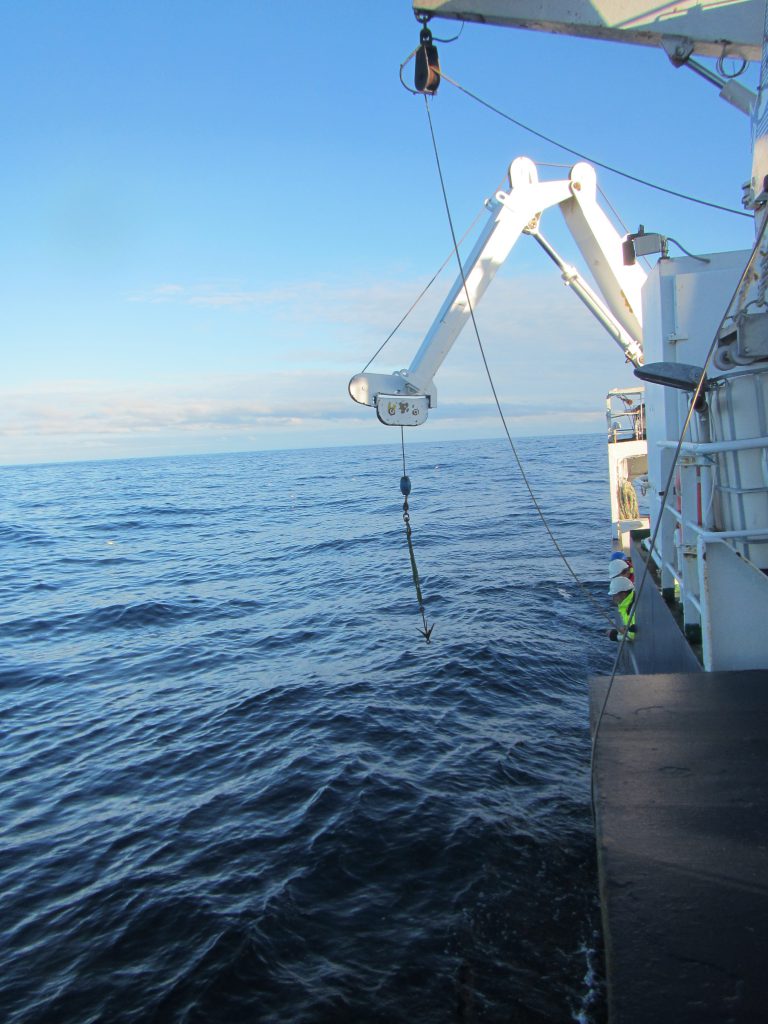
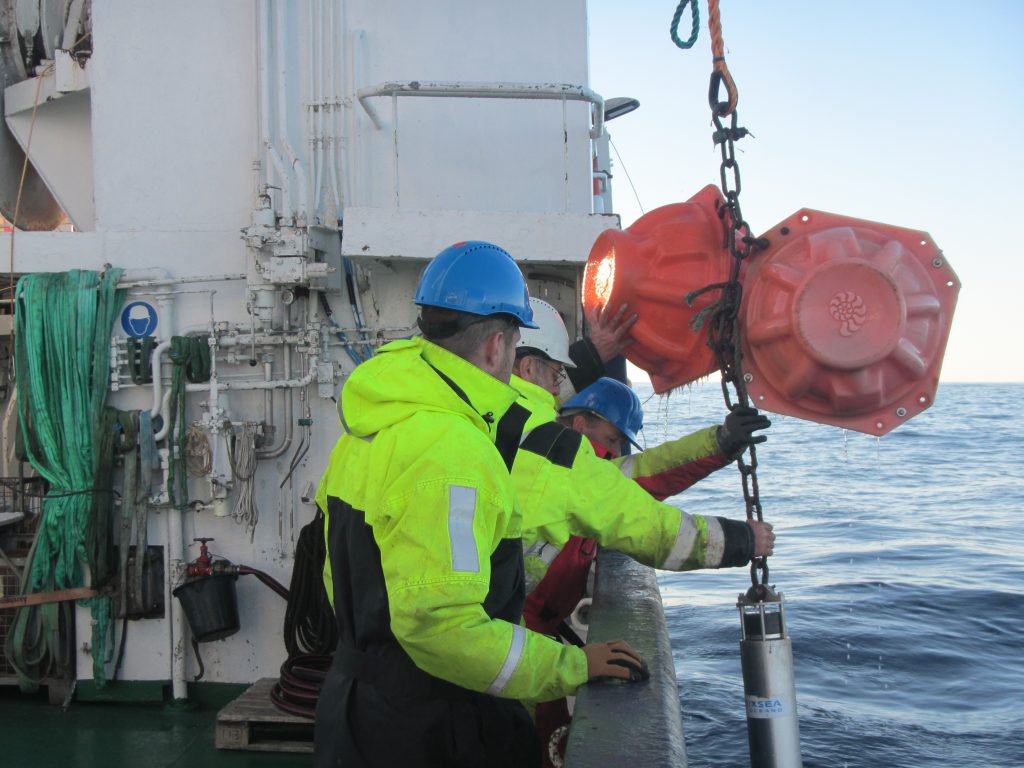
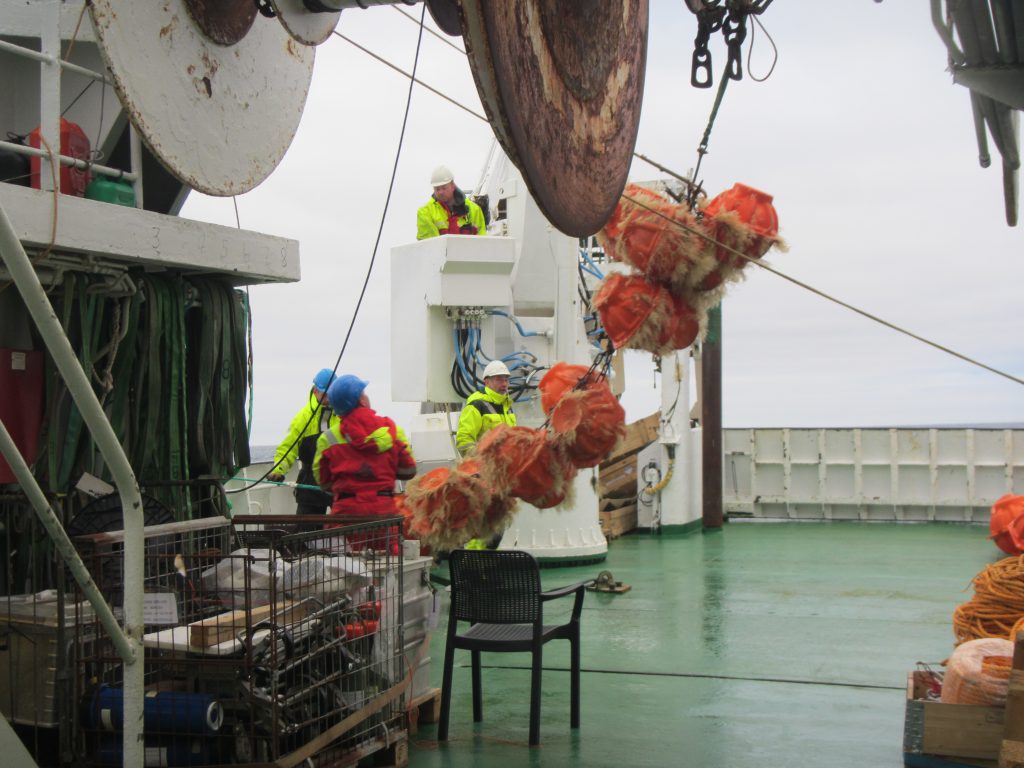
Below we see orange buoyancy floatation thingies being lowered into the sea, and still on deck there is an acoustic current meter that will be next.
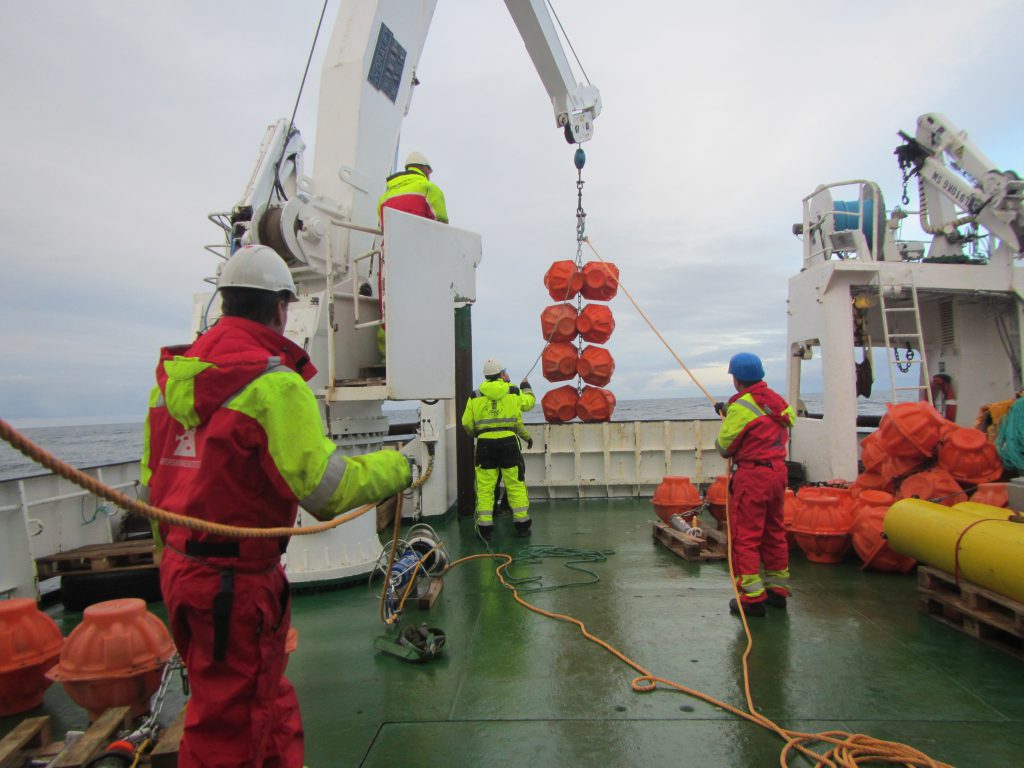

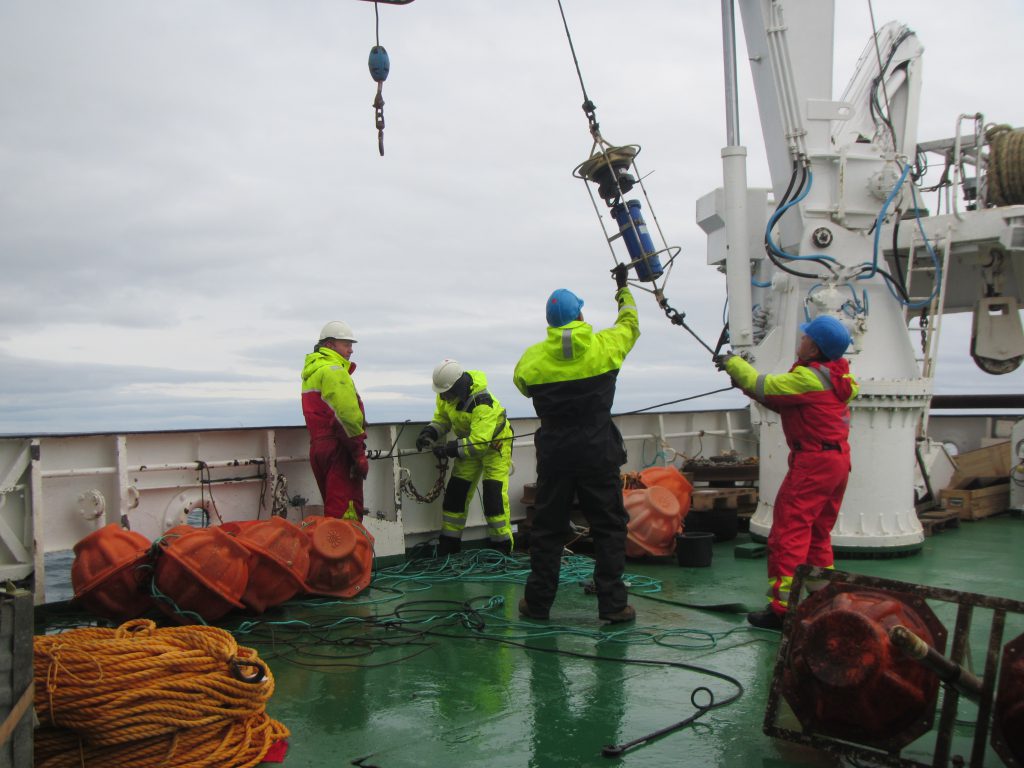
One thing I found super interesting on this cruise was to see the different generations of instruments all in use. For example, what we see being lowered into the sea in the picture below, above those orange flotation thingies, is a rotating current meter, predecessor to the acoustic current meter we saw in the image above. Rotating current meters work pretty similar to how we measure wind at home weather stations: The red vane will position the instrument in the current and the little wheel will turn with the current. Both the orientation of the instrument and the rotations of the wheel will be recorded.
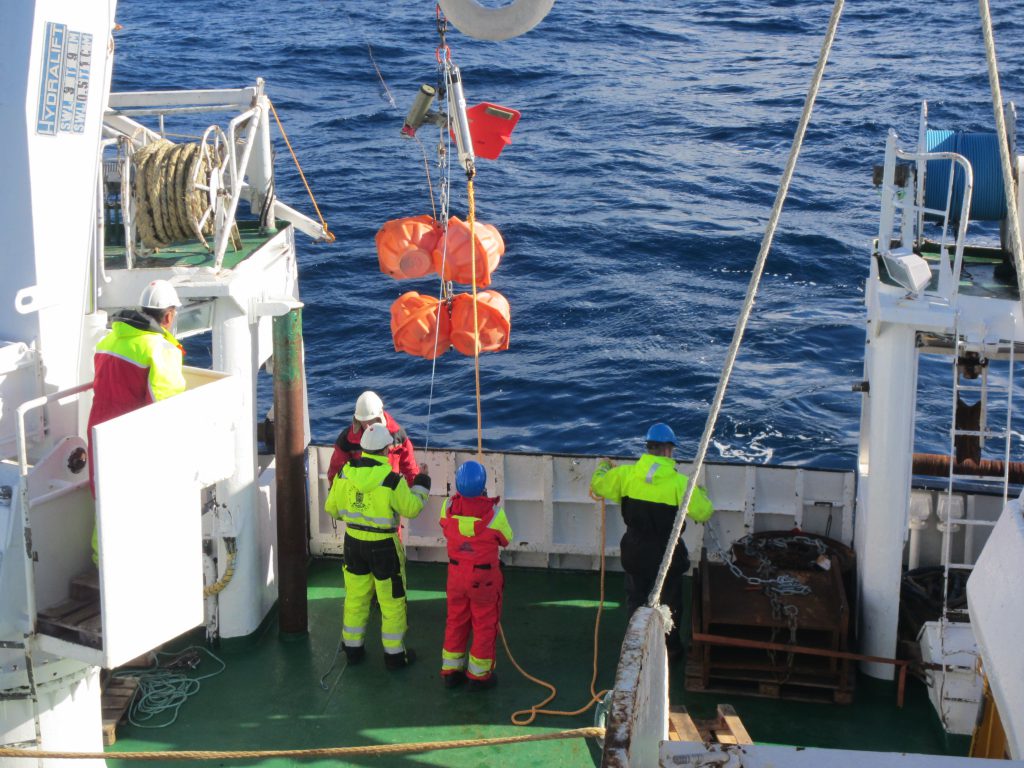

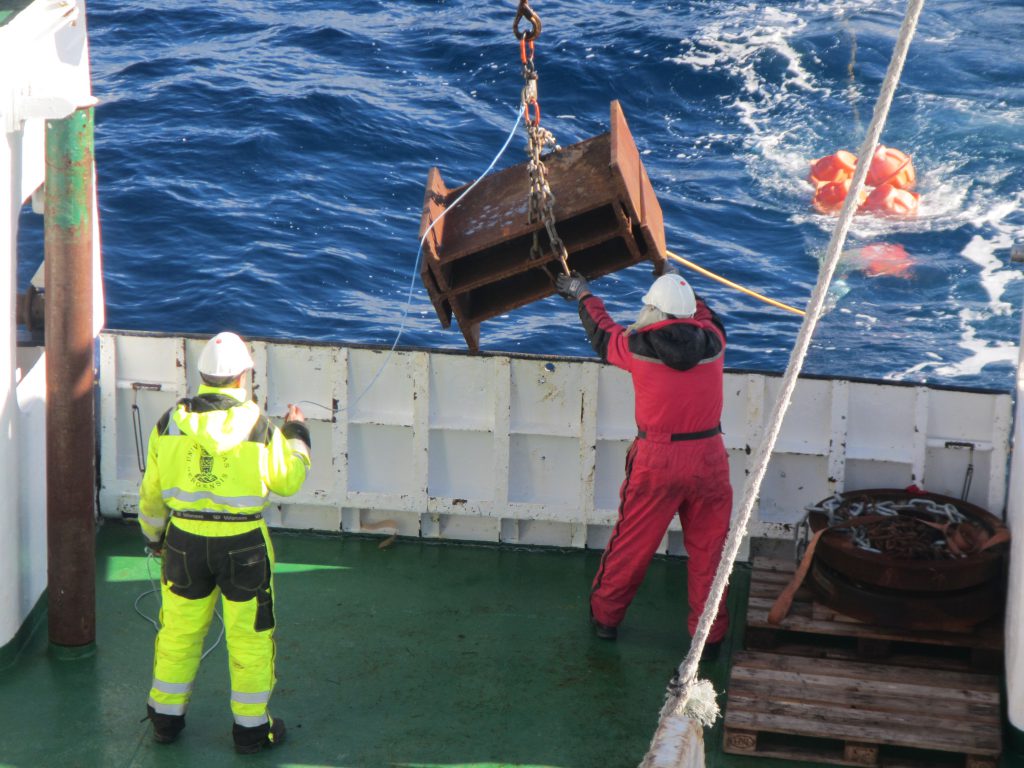
When all the instruments and orange floatation thingies are attached to the rope and it has all been lowered into the sea, everything is still floating on the surface. The final act is to drop the anchor that will pull everything under water and in an upright position. This, again, requires a lot of precision, because where the anchor is dropped determines the position in from all the data is going to be collected. So the way this works is that the ship is steaming pretty slowly towards the target position while instrumentation, floatation thingies and rope go over board, and if everything is timed well, by the time everything is out in the sea, the final position has been reached and the anchor can go out.

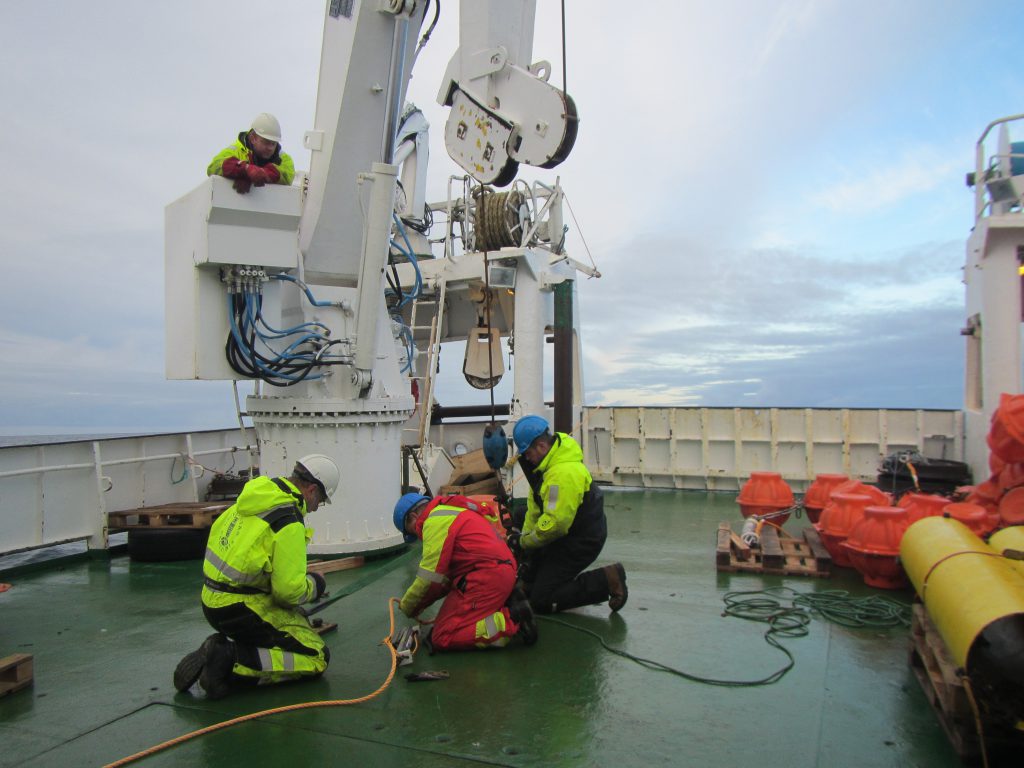
Exciting stuff! One mooring we even deployed before breakfast (and I am showing this mainly because I like the colors in this pic).

Next post will be on: So now how do we get those things back on deck again after their stint out at sea?



















