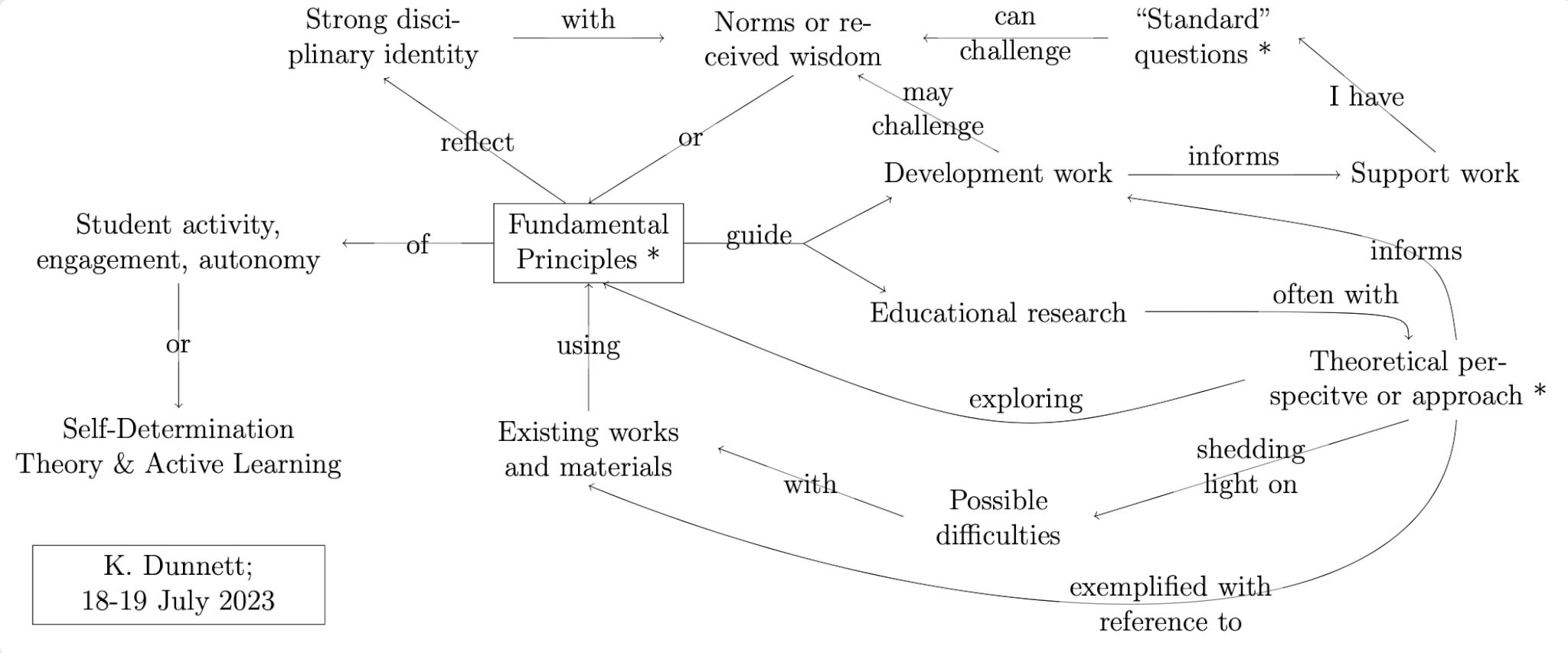
Exploring PBL, reflection, student identity, and sustainability in Ginie Servant-Miklos’ work
I am currently in the early stages of co-developing a course, most likely project-based, on sustainability for engineering students. I have written a lot about how I am trying to make sense of key competencies in sustainability and how to assess them, but then I recently stumbled across a Future Learning Design podcast interview with […]