
Separating signal from noise
It might hinder student learning when demonstration with a low signal-to-noise ratio are shown.
In this post, I talked about the Roth et al. (1997) paper on 6 dimensions that might hinder student learning from demonstrations. One dimension that I have neglected in the past is the one about “separating signal from noise”.
This dimension is about how all observation is interpreted, and that it depends on existing understanding and its interplay with the world. Students perceive science demonstrations from a different perspective than that of teachers and scientists.
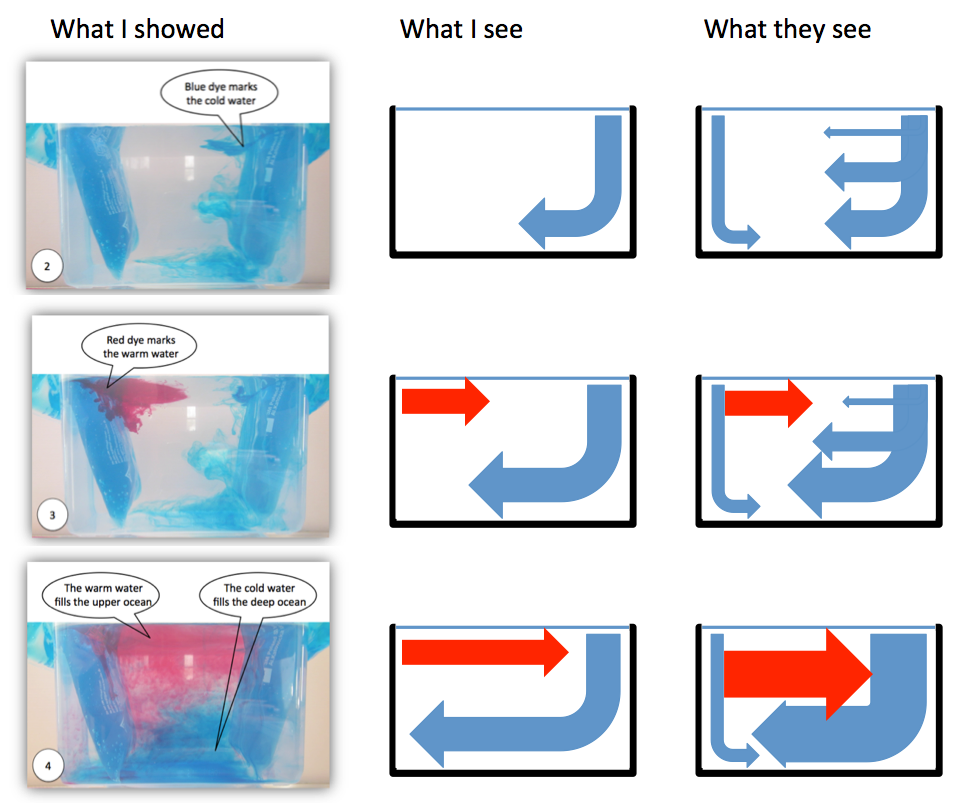
I am definitely guilty of assuming that students see what I want them to see. One example of where this might totally not have worked in the figure below.
The left column in the figure above is taken from an instruction for educators and parents of primary school kids I wrote a while back. When taking the pictures I was aware that the quality in terms of signal-to-noise was not very good (and in fact people [i.e. my parents] even told me). In my defense: The pictures of this experiment I shared on this blog are all less noisy, and I even explicitly addressed and discussed some of the noise! But still, only when reading that article today I fully appreciated how difficult it might be to see the signal through the noise (especially when the speech bubbles in the picture don’t even point exactly to the right places!), and how distracting it probably is when I implicitly assume that students see the signal and even start discussing the noise more than the signal.
So what we see above are, in the left column, the pictures I originally shared in that manual. In the middle column, I’m showing what I see when I look at the pictures on the left. And then in the right column I’m drawing what people might be seeing when looking at that same experiment. No idea if that really is what students see, but looking at the pictures now, there is actually no reason why they should see what I see. See?
One indicator of the signal-to-noise ratio and of what students actually perceive as important can be found in the three little essays the primary school kids wrote after my visit in December 2012: Two out of the three explicitly mention that I used a yoghurt beaker as heating on the one end of the tank (while the third only refers to a beaker). Clearly that seems to have been a very important observation to them.
So what do we learn from this? I, for one, am going to make sure to pay more attention to the signal-to-noise ratio when showing demonstrations. And if there happens to be a lot of noise, I am going to make it a lot clearer which part of the signal is actual signal, and which is noise. Lesson learned.
Leave a Reply
Share this post via
Why might students not learn from demonstrations what we want them to learn? - Adventures in Oceanography and Teaching says:
[…] Separating signal from noise 2) Different discourses 3) Interference from other demonstrations 4) Switching representations 5) […]